Xiaomi SU7: the little rice company did what the big fruit company couldn't!
Who is Xiaomi?
Most people outside China might have never heard of Xiaomi, a Chinese consumer electronics company that was founded 14 years ago on April 6, 2010. Back then, the company designed and manufactured cheap Android smartphones, which it only sold through online flash sales.
Fast forward just four years and by 2014, Xiaomi was already the leader in the fiercely competitive Chinese smartphone market. Less than a decade later, the company became the world's third-largest smartphone manufacturer (behind only Apple and Samsung)! However, you would be incorrect to assume that smartphones are all that Xiaomi currently has to offer.
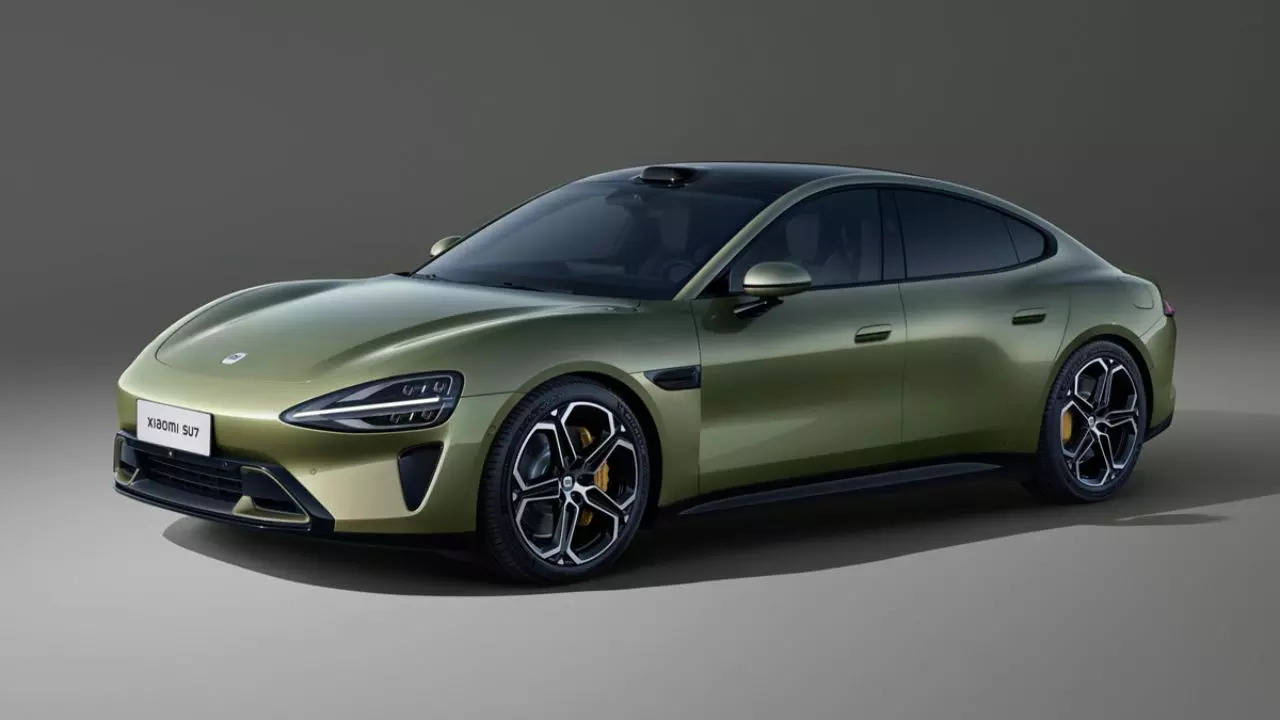

The Xiaomi SU7 electric sedan
How did Xiaomi become a carmaker?
Over the last few years, Xiaomi has been quietly building its "Human x Car x Home" smart ecosystem that brings together personal devices, smart home appliances, and automobiles through its HyperOS operating system (formerly known as MIUI, or me-you-I). The company offers an interesting range of smart home products that not only includes televisions and set-top boxes/streaming sticks, but also WiFi routers, security cameras, electric scooters, robot vacuum cleaners, smart fish tanks, and even drones!
Xiaomi's latest product is its most ambitious ever, and it has instantly catapulted the "little rice" company (that's what Xiaomi means) to the upper echelons of global electric vehicle manufacturers. The Xiaomi SU7 (which stands for Super Ultra 7) is a battery electric sedan that the company launched on March 28, 2024. It was designed by Li Tianyuan (formerly at BMW) and James Qiu (formerly at Mercedes Benz), with American car designer Chris Bangle (who served as Chief of Design for BMW Group) serving as a consultant. The car is being contract manufactured in China by the state-owned Beijing Automotive Industry Holding Company (BAIC). You would be forgiven for thinking that it looks eerily similar to the Porsche Taycan because that is incidentally one of the two electric sedans it was benchmarked against (the other one being the Tesla Model S).
Why is the SU7 revolutionary?
The SU7 is a four-door sedan that is available in three versions, with rear wheel drive and all wheel drive configurations. The base SU7 comes with rear wheel drive and a 73.6 kWh battery that delivers a driving range of 700 km (435 mi). The mid-spec SU7 Pro gets a 94.3 kWh battery that boosts the range to a whopping 830 km (516 mi). The top of the line SU7 Max comes with a 101 kWh battery, with a slightly lower range of 800 km (497 mi) due to the addition of all wheel drive. In terms of performance figures, the base SU7 accelerates from 0-100 km/h (or 0-62 mph) in 5.3 seconds and can achieve a top speed of 210 km/h (130 mph). The SU7 Max can do the 0-100 km/h run in just 2.8 seconds and has a top speed of 265 km/h (165 mph). The car also has a drag coefficient of 0.195 Cd, which makes it the most aerodynamic production car in the world!
It is simply unbelievable that a 14 year-old Chinese company has managed to do what even a technology behemoth like Apple failed to do - design and build one of the world's best electric cars. What's even more mind blowing is that Xiaomi has priced the SU7 competitively at CNY 215,900-299,000 (approximately USD 30,000-40,000). That price has not only enabled it to undercut the widely popular Tesla Model 3 in China by CNY 30,000, but also achieve a market valuation of $55 billion, which is higher than that of US automakers Ford and General Motors!

Interior of the Xiaomi SU7
What is the market response to the SU7?
The Xiaomi SU7 received 88,898 pre-orders within 24 hours of launch, with customers paying a deposit of CNY 5,000 (USD 850) to reserve their car. While the company has stated that deliveries will begin by the end of April 2024, an anticipated surge in pre-orders could result in customer wait times of at least seven months. Furthermore, the BAIC plant where the SU7 is being manufactured currently has an annual production capacity of 150,000 vehicles, which means that it can only produce 100,000 vehicles in the remaining 8 months of this year (note that car manufacturers also have to shut down their plants for a two-week annual maintenance in December).
It is unlikely that we will see the Xiaomi SU7 being sold outside China, as both the European Union and the US are investigating claims that made-in-China electric vehicles received an unfair competitive advantage in overseas markets due to Chinese government subsidies (which could have also helped Xiaomi undercut Tesla). The US is also looking into reports that connected cars made by Chinese companies could collect sensitive information about their drivers and pose risks to national security.
Why did Xiaomi succeed where Apple failed?
It is extremely hard to design/build a car, even if you are the world's most valuable technology company with the finest talent at your disposal. Apple had been reportedly working on an electric self-driving car since 2014, under the codename "Project Titan". While the company never publicly stated that such a vehicle was in development, there were reports that thousands of employees had been internally assigned to the project.
Apple CEO Tim Cook has said that their focus on integrating hardware, software, and services across its existing product lines is what makes magic happen at the intersections, but this proved to be a challenge when designing a car. While the Xiaomi SU7 uses readily available chips from international suppliers such as Qualcomm and NVIDIA, Apple reportedly tried to design its most advanced "neural" processor, with four times more compute power than the M-series chips that the company created for its Mac and iPad product lines. The processor was also believed to have been capable to handle the complex AI workloads needed for a fully autonomous vehicle.
During 2021-2022, Apple approached several leading automobile manufacturers such as Volkswagen, Hyundai-Kia, and Nissan to secure a partnership for contract manufacturing the Apple Car. However, none of them were willing to share their electric vehicle platforms for building such a vehicle due to concerns about its branding. Meanwhile, Xiaomi developed an in-house platform called Modena (paying homage to the Italian hometown of Ferrari) that supports both 400-volt and 800-volt architectures with multiple motor and battery combinations.
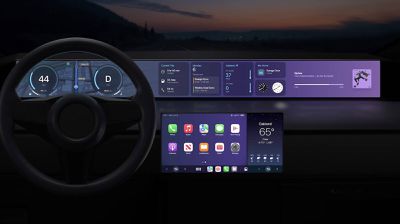
Next-generation CarPlay
Without a dedicated platform, Apple could no longer develop its own autonomous electric car. However, it is likely that the company's software teams might have already worked on the infotainment system for this doomed project. In a smart move, Apple revealed the next-generation of CarPlay at its 2022 Worldwide Developers Conference and announced that it would support multiple displays within a vehicle, including instrument clusters. Due to a deeper integration with the vehicle's hardware, this new CarPlay could display a speedometer, fuel level, and temperature gauge, while also offering built-in climate controls, radio controls, and widgets in the instrument cluster. At first glance, all of these features appeared to have been designed for the rumored Apple Car that never came. Apple said that all processing would happen on the connected iPhone, and 14 automobile manufacturers committed to offering this CarPlay in their new vehicles.
Almost two years later though, Apple's next-generation CarPlay is yet to be seen in any new vehicle. This failure of the company's last ditch effort to leave its mark on the automobile industry might be an indication that it has finally given up on its dreams to design and build an electric car. After all, while Xiaomi might have been called the "Apple of China", Apple certainly is not the "Xiaomi of the US".

Comments
Post a Comment